Kidney Stones: its symptoms, causes, and treatment

Medically Reviewed By
Dr Divya Rohra
Written By Prekshi Garg
on Jun 2, 2022
Last Edit Made By Prekshi Garg
on Mar 17, 2024
We're hearing this word! Do you know how it works? Why is it important? We will share detailed information about your body's bean-shaped organ (Kidney).
Your Kidney's main function is to clean toxins and waste products like urea, acids, and creatinine. Every minute your Kidney filters a half cup of blood. Your Kidney also maintains a healthy balance of water, salts, and minerals in your blood.
Let's know how multitasking your Kidney is.
Roles your Kidney is playing:
Your Kidney plays a vital role in keeping your body functioning properly; therefore, taking care of them is vital.
- Your Kidney controls the pH balance of your blood.
- If your body doesn't have enough sugar (glucose), your Kidney makes it.
- To increase blood pressure, your Kidney makes renin, a protein.
- Help your body make red blood cells, absorb calcium, and produce erythropoietin and calcitriol.
- It helps to control metabolism and reduce inflammation.
- Ensure that kidneys maintain body fluid at the correct levels.
- It keeps your boons strong and healthy.
From the above, it is clear that the liver has a significant role in proper body functioning and overall wellness. So, be aware of what your body is telling you about it.
Some of your daily habits and other diseases can cause affect its functioning and lead to infections and diseases.
Factors that cause kidney diseases:
Some common habits that can cause kidney diseases.
- Smoking: "Smoking is injurious to health," but let's know why? Smoking damages blood vessels by slowing blood flow to the kidneys, which can result in kidney disease.
- Excessive consumption of alcohol: Drinking excessive alcohol can put additional strain on your kidneys and, over a while, can impact your kidney function and lead to chronic health conditions.
- Unhealthy diet: Diets high in salt, sugar, saturated fats, and high dietary protein intake may result in kidney hyperfiltration, glomerular injury, and proteinuria.
- Delaying bathroom breaks: Long-term kidney and bladder problems can result from holding your urine for a long time by tightening the sphincter against a stretched bladder, which can thicken the bladder wall and disrupt the natural one-way mechanism of urine flow from the kidneys into the bladder.
- Toxins and chemical exposure: Your kidneys filter chemicals, poisons, and prolonged exposure can negatively affect the kidneys and bladder.
- Less sleep: Disturbed sleep patterns can also influence kidney health and lead to chronic diseases.
These are some of the daily habits that can cause kidney diseases. Now let's look at some common kidney diseases.
Some common kidney diseases
- IgA nephropathy: It is one of the common diseases caused by diabetes or high blood pressure. It can occur at any age, but mostly in teenagers and adults. It damages the glomeruli inside your Kidney and causes kidney diseases.
- Chronic kidney diseases: Chronic kidney diseases or chronic kidney failure involve a gradual loss of kidney function and cause dangerous levels of fluid, electrolytes, and waste to build up in your body. Decreased mental sharpness, sleep problems, urinating more or less, muscle cramps, swelling of ankles and feet, dry/itchy skin, high blood pressure, and chest pain are common symptoms of CKD.
- Acute kidney injury (AKI): Acute kidney injury (AKI), or acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden episode of kidney damage that happens within a few hours or a few weeks. It makes it hard for your kidneys to keep the right fluid balance in your body by causing a build-up of waste products in your blood. It also affects the brain, heart, and lungs.
- Glomerulonephritis: When tiny filters inside your Kidney get damaged results in glomerulonephritis. Toxins, medication, and viral infections such as HIV, hepatitis B, and C virus also cause glomerulonephritis.
- Polycystic kidney disease (PKD): Polycystic kidney disease is a cluster of cysts that develop primarily within your kidneys and cause your kidneys to enlarge and lose function over time. Having large or high numbers of cysts can damage your kidneys.
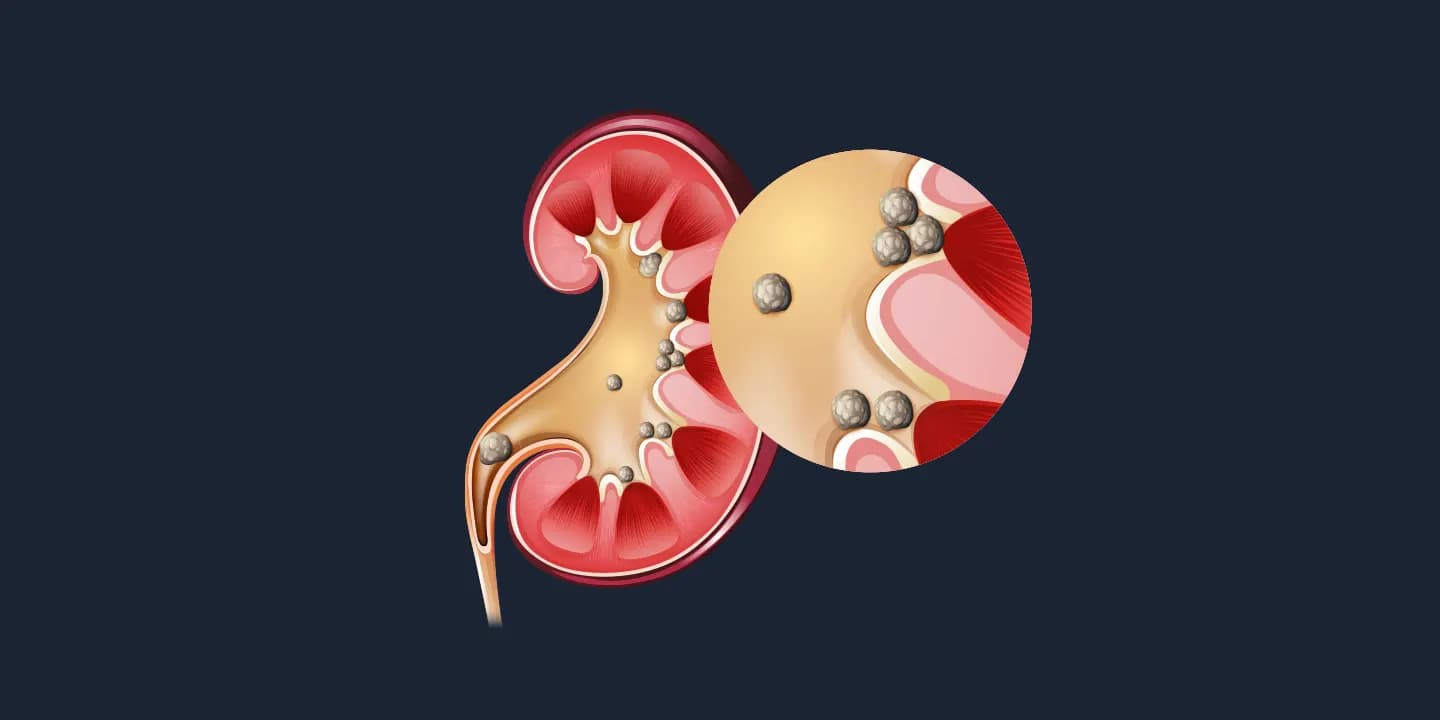
- Kidney stones: High dissolved minerals and salts can form stones in your Kidney. It can be small as a grain of sand and big as a golf ball. They block the flow of urine and cause infection, kidney damage, or even can cause kidney failure.
These are some common kidney diseases, but there are more, and every condition requires different treatments depending on the type, severity, and other factors. There are various tests available to help diagnose the diseases.
Common Blood Test for Kidney:
Your healthcare professional may use your medical history, physical exam, and test to diagnose your kidney infection. Some common tests for kidney infection are:
- Kidney Function Tests: Kidney function tests help to measure the efficiency of your kidneys and check how well your kidneys clear waste from your system. These tests can estimate your glomerular rate (GFR), which tells how quickly your kidneys are clearing waste from your body.
After Kidney Function Blood Test, you may feel dizziness, bruising, and fatigue, but these typically do not cause long-term complications.
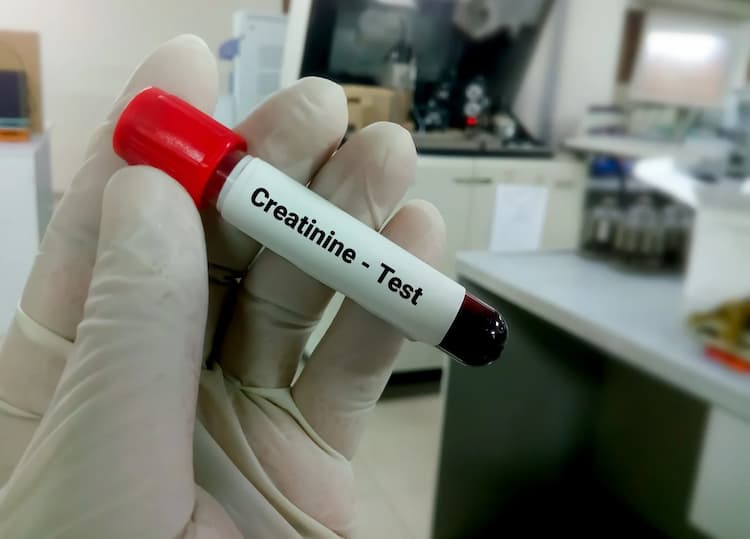
- Creatinine Test: Creatinine is a chemical byproduct of muscle energy-generating mechanism. Healthy kidneys remove this substance from the blood, and the amount of creatinine in your blood tells how well your kidneys function.
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) Test: Urea nitrogen is a waste product that your Kidney removes from your blood, and this test measures the amount of urea nitrogen in your blood. If your BUN level is high, your kidneys are not working well.
- Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR) Test: Glomerular is tiny filter of your Kidney. GFR shows how well your kidneys are filtering. When the glomerular filters less blood, dangerous toxins can build up in your body and damage your kidneys. Early diagnosis can help you take preventive steps to protect your kidneys.
- Albumin Blood Test: Albumin is a protein made by your liver, which helps measure the amount of albumin in your blood. A low albumin level might result from kidney disease, liver disease, inflammation, or infection, and high albumin levels result from diarrhea.
These are some common tests for kidney infection, and the type of test right for you depends on the type of infection and symptoms you're experiencing. Individuals with underlying diseases or risks, like high blood pressure, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or a family history of kidney failure, must take a kidney function test. You should incorporate routine KFT in your life even if you are healthy, as it helps keep track, identify problems even before the symptoms appear, and allow you to manage them in time.
Redcliffe Labs offers a variety of blood tests for Kidney. We provide free home sample collection convenience, so you will not have to travel to our diagnostic centers. Book your Blood Test for Kidney in Delhi now with Redcliffe Labs to avoid severe conditions.
![RFT Test - Price, Purpose, Procedure, Results [2024]](/myhealth/_next/image/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fmyhealth-redcliffelabs.redcliffelabs.com%2Fmedia%2Fblogcard-images%2FNone%2Fcda1f900-5908-4ca0-b18b-0a9c7882c0f9.webp&w=750&q=75)