Monkeypox: Symptoms and Treatment

Medically Reviewed By
Dr. Ragiinii Sharma
Written By Srujana Mohanty
on May 15, 2022
Last Edit Made By Srujana Mohanty
on Mar 17, 2024
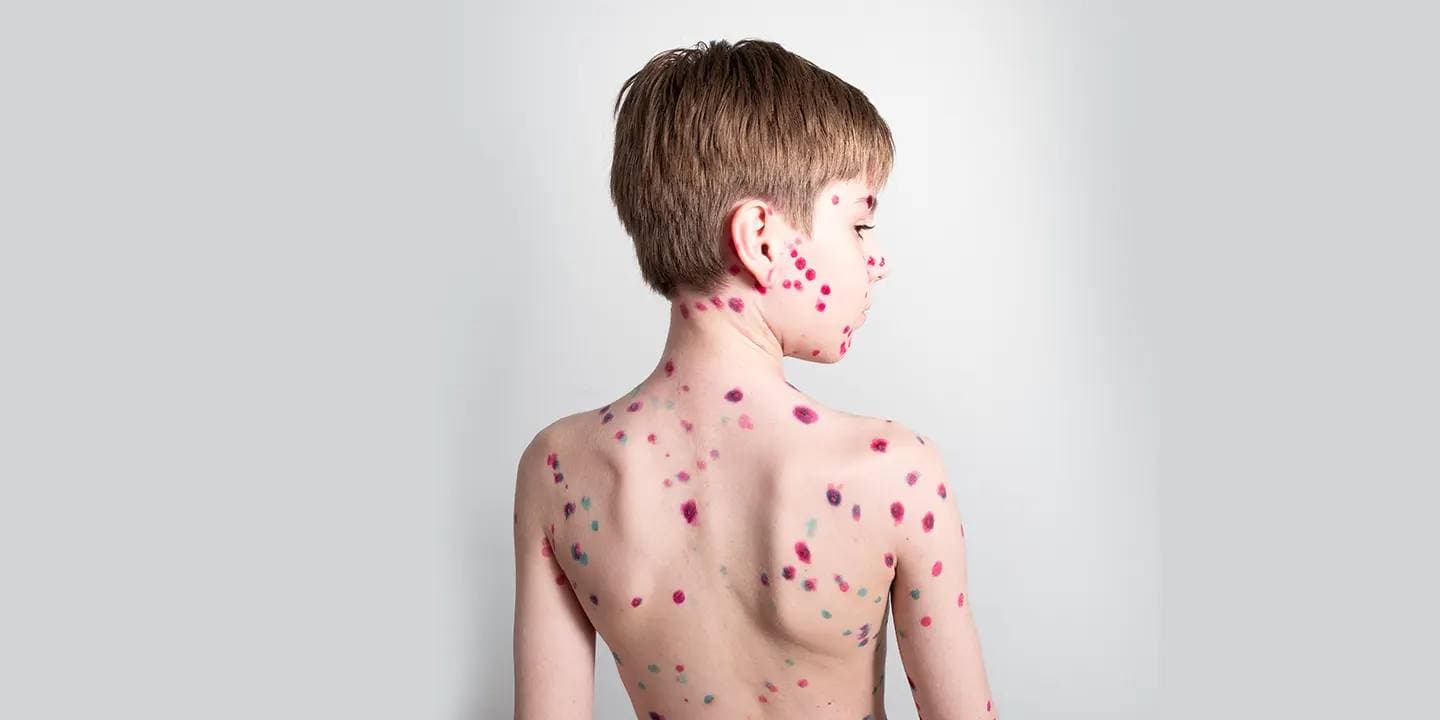
Monkeypox is a rare disease in India. The cases of monkeypox have been reported in places like Benin, Central African Republic, Cameroon, Côte d’Ivoire, Gabon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Liberia, Republic of the Congo, Nigeria, South Sudan, and Sierra Leone. Amongst these places, the maximum cases of monkeypox have been reported in the rural areas of Democratic Republic of Congo. The disease monkeypox was first diagnosed in a group of monkeys in 1958 in a laboratory. Monkeypox was first reported in humans in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo. In this article, let’s talk about what is monkeypox, what are the symptoms of monkeypox, how is monkeypox treated, use of smallpox vaccine against monkeypox, side effects of the smallpox vaccine, and how the spread of the virus can be prevented. 
What is Monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a rare, zoonotic disease that is caused by the infection of the orthopoxvirus, a member of the family Poxviridae. Zoonotic diseases are the ones that can be transmitted from the animals to humans, humans to animals, and even from human to human. This disease belongs to the same family as smallpox. The occurrence of this disease is more prominent in the areas of tropical rainforest of Central and West Africa. The disease can be fatal in some cases and deaths are more common in the younger population. When the infection of the virus is transferred from the animal to the humans, it is known as primary transmission, and when the infection is transferred from human to human, it is known as secondary transmission. Primary transmission usually occurs when you come in contact with the bodily fluids, blood, mucosal lesions, or cutaneous lesions of infected animals. Consumption of inadequately cooked meat and other animal products can also cause the transmission of the virus from animals to humans. Secondary transmission usually occurs when you come in contact with the respiratory secretion and skin lesions of infected persons or objects that have been contaminated with the virus.
What are the symptoms of monkeypox?
According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the symptoms of monkeypox and smallpox are quite similar, however, the severity of symptoms in the former is milder than the later. The only difference observed between the symptoms of monkeypox and smallpox is that the lymph nodes in monkeypox swell leading to lymphadenopathy. It might take around 5 - 21 days for the symptoms of monkeypox to appear in healthy individuals. The illness may last for around 2-4 weeks. The early signs of monkeypox include:
- Headache
- Fever
- Backache
- Muscle aches
- Chills
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Exhaustion
- Rashes that develop after 1-3 days of getting a fever. These rashes often emerge on your face and then gradually spread in the other parts of your body as well.
- Lesions also develop that pass through five stages before falling off. These stages include macules, papules, vesicles, pustules, and scabs.
What is the treatment available for monkeypox?
 In the present times, there is no treatment available for monkeypox. The good thing is that monkeypox is in itself a self limiting disease, that is, it gets better with time without the need of any treatment or medicines. However, certain vaccines are used to control the spread of the disease among the population. Since, monkeypox and smallpox are so similar to each other, therefore, currently the vaccines for smallpox (vaccinia vaccine) are used to control the transmission of monkeypox. According to research, people who have already been vaccinated with smallpox are comparatively less prone to monkeypox. Other methods that help control the disease include vaccinia immune globulin (VIG), and antiviral medications (used generally in case of animals and not humans). Recently a vaccine has been approved in 2019 that is known to protect against both smallpox and monkeypox. However, the vaccine is still not available to the masses.
In the present times, there is no treatment available for monkeypox. The good thing is that monkeypox is in itself a self limiting disease, that is, it gets better with time without the need of any treatment or medicines. However, certain vaccines are used to control the spread of the disease among the population. Since, monkeypox and smallpox are so similar to each other, therefore, currently the vaccines for smallpox (vaccinia vaccine) are used to control the transmission of monkeypox. According to research, people who have already been vaccinated with smallpox are comparatively less prone to monkeypox. Other methods that help control the disease include vaccinia immune globulin (VIG), and antiviral medications (used generally in case of animals and not humans). Recently a vaccine has been approved in 2019 that is known to protect against both smallpox and monkeypox. However, the vaccine is still not available to the masses.
Vaccine
The smallpox vaccine that provides protection against monkeypox as well is made using the causative agent of cowpox, that is, poxvirus. All these three viruses belong to the same family, poxvirus, and are thus very similar to each other due to which a single vaccine can provide protection against these viruses. Cowpox is a cow disease and does not infect humans, therefore, it is safe to use this virus in humans. Smallpox is the first vaccine to be developed and it was the idea of Edward Jenner to use the cowpox virus against smallpox in 1796.
Idea behind the vaccine
The smallpox vaccine was invented by Edward Jenner by a simple observation. He observed that the ladies of his region who milked cows did not develop the smallpox infection, when the virus spread across the English countryside. This made him think that there might be some infection in the cow that might get transferred to the women through the blisters on the udders of the cows during milking. Thus, with this observation, he injected the fluid obtained from the blisters of cows into the people of his region. This is how the first vaccine was developed in 1796. The World Health Organisation (WHO) declared smallpox as an eradicated disease in 1980. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), the effectiveness of the smallpox vaccine to control the transmission of monkeypox is around 85%.
What are the side effects that can occur during the treatment of monkeypox?
People are protected from monkeypox infection, by the use of smallpox vaccine. There are certain side effects that may occur when you are given the vaccine, however the occurrence of these side effects is very rare. The side effects that may occur include:
- Swelling in the heart or the tissues that surround the heart
- Chest pain
- Irregular or fast heartbeat
- Breathing issues
- Swelling in the spinal cord or the brain
- Infection of a bacteria at the site if vaccination
- Chances of spreading of the virus to other parts of the body or to other people as well.
- Anaphylaxis, that is, severe allergic reaction
These side effects do not generally appear in people. However, there is a certain group of people who are more prone to the development of these side effects. The people at a higher risk of developing side effects include:
- Skin diseases like atropic dermatitis (eczema)
- Heart issues like stroke, congestive heart failure, and heart attack
- Have a family history of heart problems
- If you are a regular or heavy smoker
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- High blood sugar level, that is, diabetes
- If your age is less than 1 year old
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding stage
- Allergic response to certain medicines like polymyxin or neomycin
How can we prevent the spread of monkeypox?
Prevention is always better than cure. Therefore, it is better that you take measures to prevent getting the infection, instead of looking for a treatment option after you are infected. Also, since monkeypox is not treatable, it is better you take measures to prevent the infection. Here are certain tips that you can follow to prevent the transmission of these diseases.
- Keep your hands clean. Wash them with soap and water at regular intervals.
- Use a sanitizer in places where water is not available to wash hands.
- Avoid going near stray, wild, unwell, or dead animals as monkeypox can be transmitted from animals to humans.
- Do not consume bush meat, that is, a meal made from wild animals.
- Do not share your bedding or towels with people who are suspected to be infected with monkeypox.
- Avoid close contact with people who are infected with monkeypox.
Takeaway
Monkeypox is a rare disease, however, one should be cautious against such infections as they can easily transmit among the population. Now that you know the symptoms of the disease, make sure that you take a doctor's consultation if you observe these symptoms in yourself. As discussed earlier, prevention is better than cure, therefore, make sure that you follow a hygienic lifestyle and stay aways from animals who look unwell. As far as the treatment is concerned, monkeypox is a self treatable disease. Apart from this smallpox vaccine can play a significant role in combating the transmission of the disease. Therefore, be cautious of your surroundings to stay safe from such viral infections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Can monkeypox be cured?
Monkeypox is a self curable disease, that is, it gets cured on its own in some time without the need of any medicines. -
What happens if you get monkeypox?
You might experience the following symptoms, if you are infected with monkeypox:- Headache
- Fever
- Backache
- Muscle aches
- Chills
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Exhaustion
- Rashes
- Lesions
-
How does a person get monkeypox?
You can get monkeypox if you come into close contact with an animal that is unwell or another person who has been diagnosed with monkeypox.