What Is Anemia? Causes, Symptoms & Treatment

Medically Reviewed By
Dr Divya Rohra
Written By Komal Daryani
on May 5, 2022
Last Edit Made By Komal Daryani
on Mar 18, 2024
Key Facts -
- Anemia is a common and yet serious blood disorder affecting millions worldwide.
- In most cases, anemia has mild or no symptoms but affects the quality of living
- A leading cause of anemia is a lack of nutritional diet.
- Iron-deficient anemia is the most common type of anemia.
- As per the WHO report, 40% of pregnant women and 42 % of children are anemic worldwide.
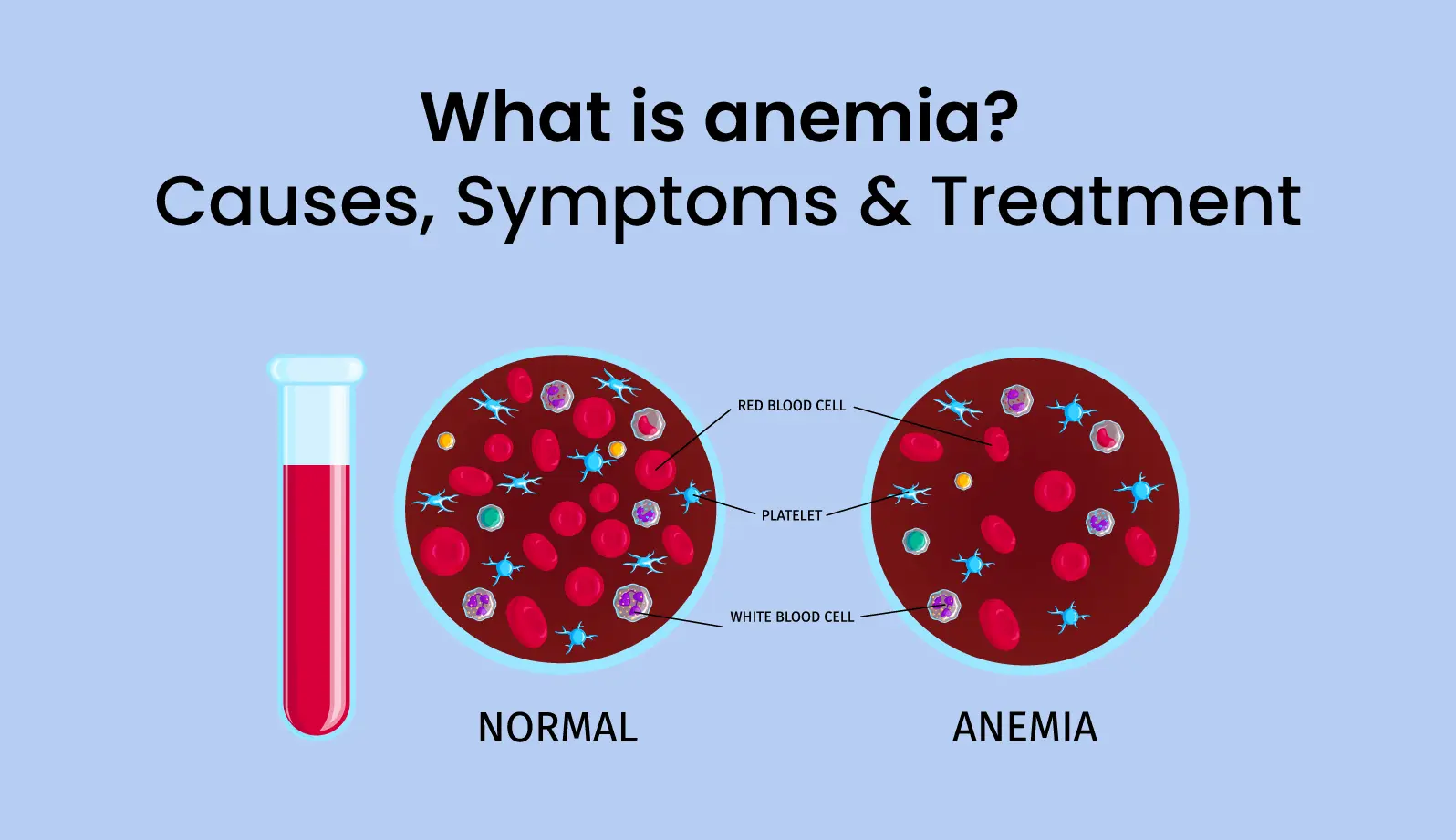
What Is Anemia?
Anemia is a common blood disorder affecting all age groups irrespective of sex, but it is most prevalent in women of reproductive age and children.
It is a condition in which your healthy red blood cells and haemoglobin concentration are low, affecting the capacity of blood to carry oxygen to the body's tissues. When the body's tissues receive less oxygen your body shows various symptoms such as weakness, fatigue, tiredness, restlessness in the legs, and many more.
What Causes Anemia?
Anemia is not just a diagnosis or a simple disease. There is a hidden underlying condition that shows the anemic presentation.
Anemia has a wide range of causes. There can be any of the possible causes of anemia. For example, it can occur when your red blood cells produce less in number, your red blood cells are destructing rapidly, or there is a loss of too many red blood cells.
Red Blood Cells Are Producing Less In Number-
You may suffer from anemia when your body fails to produce enough red blood cells.
Some of these conditions where the body fails to produce enough red blood cells are-
- Iron Deficient Poor Diet- Iron is an essential component in the formation of red blood cells, so if your diet is deficient in iron, it leads to more risk of less production of red blood cells.
- Poor Absorption Of Nutrients - Some diseases, diets, and medicines inhibit the absorption of essential nutrients in the body, thus impairing the production of red blood cells.
- Cancers And Their Treatments- Blood cancers like leukaemia and lymphoma affect the production of red blood cells. Also, their treatment with chemotherapy and radiotherapy impacts the bone marrow and red blood cell formation.
- Pregnancy- The volume of blood increases during pregnancy. Your body needs more blood to share with the baby, which means you need more iron and essential nutrients, but if your body lacks getting these nutrients efficiently, chances are you develop anemia.
Red Blood Cells Are Destructing Too Rapidly-
Red blood cells have 120 days of life span in the body, after which they die. But if your body destroys these red blood cells in a short span in such large numbers that even the bone marrow cannot make new healthy red blood cells, then you will suffer from anemia.
Some Conditions Increase The Destruction Speed Of Red Blood Cells Like:
- Infectious conditions like malaria
- Diseases like sickle cell anemia and thalassemias increase the destruction of red blood cells
- Immune hemolytic anemia (immune system produces antibodies against RBCs or medicines, causing RBC destruction)
Red Blood Cell Count Is Decreasing -
When your body is losing blood, you may lose large red blood cells, resulting in anemia.
The blood loss can be due to-
- Any surgery, trauma from a road traffic accident
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Chronic blood loss due to bleeding haemorrhoids, renal carcinoma, etc.
What Are The Symptoms Of Anemia?
Anemia symptoms range from person to person. Some people may have mild symptoms, while others may not have any symptoms at all.
Some of the common symptoms of anemia are-
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Paleness
- Muscle cramps
- Loss of appetite
- Altered sense of taste
- Unusual ringing in the ears
- Constant Headache
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Cold hands or feet
- Pain in the calf muscles
- Tiredness
- Restless legs
- Shortness of breath while doing something strenuous exercise or work
- Sometimes chest pain
How To Diagnose Anemia?
You are most likely to be diagnosed with anemia during a routine health checkup. To confirm the diagnosis of anemia, your doctor will ask you about detailed medical and family history, perform a physical examination, and do the necessary tests.
The most commonly used tests required for diagnosing anemia are-
- CBC & ESR- Complete blood count is a broad-scale test that evaluates red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It analyses hemoglobin as well. After evaluating the CBC results, your doctor will start your treatment.
- Transferrin Test- To rule out the type and causes of anemia, such as the Iron test (Transferrin test) to rule out iron-deficient anemia.
- Vitamin B12 & Folic Acid Levels In addition to these tests, your doctor can recommend other tests to ensure the cause of anemia.
Who Is At Risk Of Anemia?
Many people are at risk of developing anemia, and some of these conditions are-
- Having a poor diet devoid of essential nutrients and vitamins puts you at high risk for anemia.
- If you are a frequent alcoholic
- A woman in a menstruating phase loses blood every month and causes the loss of red blood cells.
- Having cancer, kidney failure, or Crohn's disease puts you at risk of anemia.
- The presence of inadequate iron and nutrients in a pregnant woman will put her at risk for anemia.
- Medication for HIV/AIDS, anti-cancer medications, and chemotherapy can also increase your risk of anemia.
What Are The Complications Of Anemia?
Anemia is related to underlying diseases, and if it goes untreated for a long time, it can lead to various serious complications.
Some of them are-
- Pregnant women with anemia can go into pre-mature labor and increases the risk of increased blood loss.
- Uncontrolled anemia mainly affects the cardiovascular system and leads to various heart-related disorders.
- Chronic anemia can weaken the immune system.
- Chronic anemia in young children hampers neurological development and also delays growth development.
- Severe anemia leads to frequent falls due to passing out and puts at risk of more traumatic injuries
- Unmanaged anemia can lead to hypotension, a condition in which our blood pressure falls to its normal value
- Severe anemia can also lead to organ dysfunction.
What Is The Management Of Anemia?
Starting early and addressing anemia correctly often leads to simple management of anemia.
To treat anemia, healthcare professionals first need to identify its underlying cause and then treat it accordingly.
Management of anemia includes:
-
- Lifestyle dietary changes to include more iron and nutrient foods
- Supplements of Iron
- Antibiotics if anemia is because of certain disease
- Hormonal balance medication if anemia is caused due to hormonal imbalance.
- If you are suffering from persistent and severe anemia, your doctor may start the medication to help stimulate red blood cells.
- If your body is rapidly destroying red blood cells, your doctor may prescribe medication to slow down the process.
- Your doctor starts the medication to suppress the immune system if your immune system is destroying the red blood cells.
- In severe anemic conditions, blood transfusions and bone marrow transplants may be recommended by your doctor.
- Surgery may be required if there is excessive bleeding following a traumatic injury.
- The ultimate treatment for anemia is to increase red blood cells and hemoglobin to improve the body's oxygen-carrying capacity and address the underlying causative factor.
What Are The Preventive Measures In Anemia?
Living a healthy lifestyle can prevent and control anemia, as well as individuals with mild to moderate hemoglobin levels, can make lifestyle changes to maintain their hemoglobin levels.
Some of the preventive measures you can follow are;
- Follow a healthy diet to ensure enough nutrients in your meal. Eat food that has enough iron, vitamin B12, folate, and vitamin C.
- Eat iron-rich foods like green leafy vegetables, beans, lentils, dried fruits, beef, and other meats.
- Take enough folate from fruits, dark leafy vegetables, green peas, peanuts, bread, cereal, pasta, etc
- Eat vitamin B-12 rich foods like dairy products and soy products.
- Vitamin C is also essential for maintaining a healthy hemoglobin level through citrus fruits, peppers, tomatoes, melons, and strawberries.
- Limit the intake of salt and added sugars
- Maintain a healthy weight
How Can We Help You Deal With Anemia?
Redcliffe Life Diagnostics provides you with all the diagnostic tests needed for anemia. All the required anemia tests like a Haemogram (CBC+ESR) are available with Redcliffe life diagnostics health packages.
Conclusion
Anemia is a common blood problem that typically affects women and children, and the most common cause is poor dietary intake. To live a healthy and happy life, it is vital to regularly monitor and check up on your health and your family members.
Disclaimer:The blog content has been posted as a piece of information and awareness only. The content provided in this blog, or in any linked materials, are not proposed and should not be taken as medical advice. Redcliffe Labs strongly recommends users to consult with their health care providers to make any medical or health-related decision.



