Normal Blood Glucose Levels & What They Indicate

Medically Reviewed By
Dr. Ragiinii Sharma
Written By Srujana Mohanty
on Jun 2, 2022
Last Edit Made By Srujana Mohanty
on Mar 17, 2024
Assessing blood glucose levels every six months for a non-diabetic patient, especially above 35, is a crucial diagnostic test to maintain overall wellness. Given the fast-paced and unregulated lifestyle that most people lead, it isn’t surprising that we often ignore alarming red flags that our body tries to show us.
Having normal blood glucose levels suggests that not only are you having good overall health, but your risks of developing Type-2 diabetes are pretty low as well. Since our blood glucose levels are a crucial determinant of our well-being, checking normal blood glucose levels is crucial.
Given the steep increase in the diagnosis of diabetes, there's no better time to get tested than now. Your sudden weight gain or weight loss might have a reason. Your tiredness might not be just because of work. Comprehensive blood tests can ascertain the underlying complication. Your quality of life depends on you and the choices you make. Prevent your health from deteriorating with early testing.
In this article we will explore more about normal blood glucose levels and what they indicate about your health.
In this Article
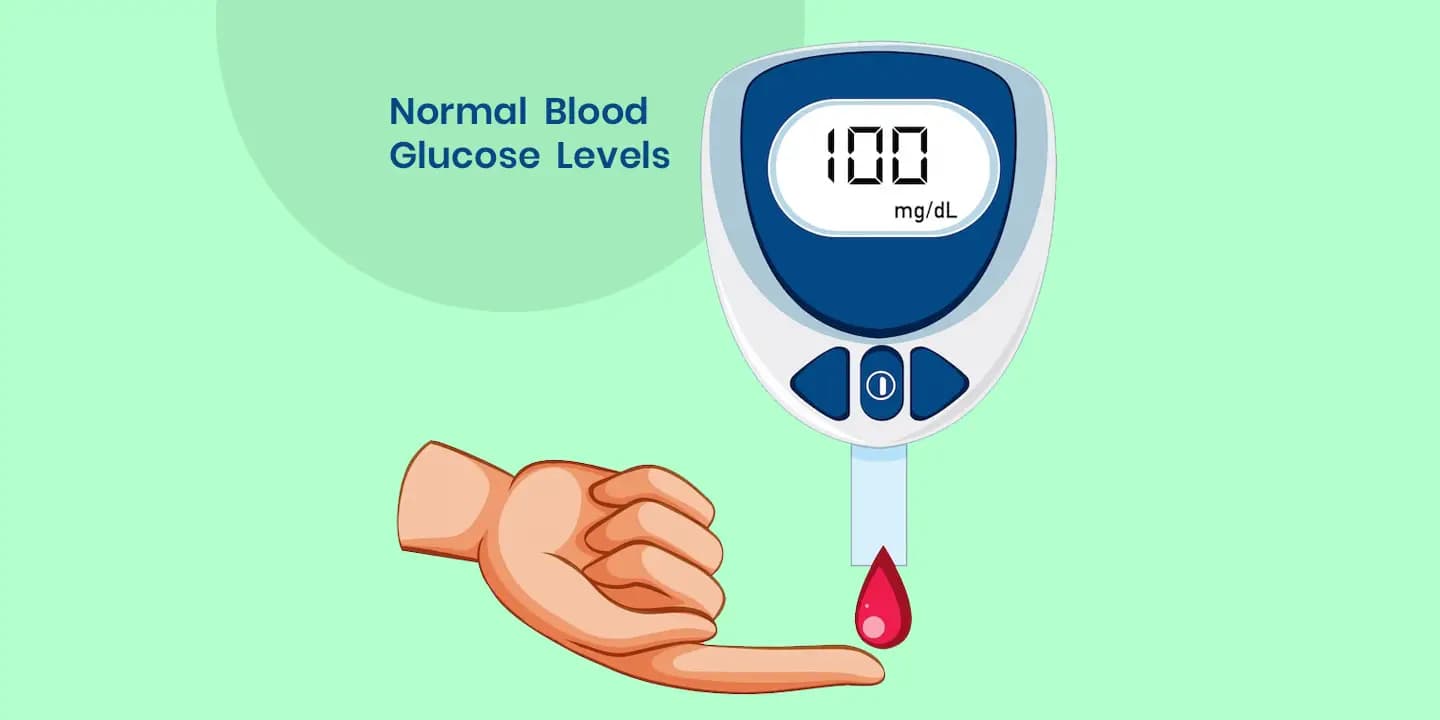
What are the Normal Blood Glucose Levels?
The blood glucose levels vary depending on a person’s age and at what time of the day they are recording the levels. Your normal blood glucose levels could also stay elevated or dipped depending on the kinds of meals that you have eaten throughout the day.
Let us walk you through the normal glucose levels depending on the age factor:
| Blood Glucose Levels in Children | |
| Type of glucose level testing | Normal range (mg/dL) |
| Fasting | 80-180 |
| Post-prandial (2 hours after a meal) | 180 |
| Before bedtime | 110-200 |
| Blood Glucose Levels in Adolescents | |
| Type of glucose level testing | Normal range (mg/dL) |
| Fasting | 80-180 |
| Post-prandial (2 hours after meal) | 140 |
| Before bedtime | 100-180 |
| Blood Glucose Levels in Adults | |
| Type of glucose level testing | Normal range (mg/dL) |
| Fasting | <100 |
| Post-prandial (2 hours after meal) | <180 |
| Before bedtime | 100-140 |
If you get a routine blood test done and the levels are low or high from the normal range, it indicated risks of diabetes or hypoglycemia. These instances require immediate medical interventions, especially if you don’t want to get undiagnosed for a serious chronic illness.
What are the Blood Glucose Tests to Check the Levels?
Every person, irrespective of being diabetic or not, should get routine blood glucose testing. Not only does it avert the risks of diabetes, but it also indicates possibilities of other underlying chronic illnesses that aren’t always diagnosed on time.
With blood glucose monitoring, several blood tests can assess the levels. Some of the most important ones include:
Fasting blood glucose test
In this test, the individual has to give their blood first thing in the morning after fasting for a minimum of 8-10 hours from the previous night. Analyzing the normal fasting blood glucose levels is a key marker for diagnosing risks of prediabetes or diabetes in the person.
Postprandial glucose test (PGT)
In this test, your lab technician will ask you to eat a filling meal at a monitored time and then give the blood sample exactly two hours after the meal's start. The post-prandial glucose test examines the efficacy of insulin in the body after a meal. If the levels are high after 2 hours of your meal, the chances are that you might have insulin resistance or your body isn’t producing or utilizing enough of the secreted insulin.
A1C or Glycated Hemoglobin test
The glycated hemoglobin test is a vital blood glucose monitoring to measure the glucose levels over the last 2-3 months. It gives an average reading of your glucose levels over the past few months to understand how your body is metabolizing the glucose levels throughout that period.
Home monitoring kits
For more accessible blood glucose monitoring, you can always opt for the home monitoring kits. They are easy to use and are also handy, especially if you don’t want to travel down to the lab to get a routine test every few months. The home monitoring kits generally include a testing strip and the needle to prick your finger and draw the blood. The blood is then transferred to the testing strip, and the machine then gives a reading of your blood glucose levels.
What are signs of High or Low Blood Glucose Levels?
With discussing the normal blood glucose levels out of the way, the next thing that you need to focus on is the signs of high and low blood glucose levels.
Even if you don’t have a formal diagnosis of prediabetes or diabetes, being mindful of the symptoms can help you prevent many complications.
Abnormal blood glucose levels indicate two cases – hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) or hyperglycemia (high blood glucose).
Some of the prevalent signs of hypoglycemia include:
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Sweating
- Shakes and chills
- Irritability
- Clamminess
- Faster heart rate
- Sleepiness
- Fainting
- Tingling in the extremities
- Pale skin, etc.
Some of the symptoms of hyperglycemia include:
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
- Feeling thirsty
- Blurred vision
- Headaches
- Weight loss
- Hard time concentrating
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Exhaustion
- Vision loss (in untreated diabetes)
If you experience any or multiple of these symptoms in a recurring manner, it is ideal to get it checked by a doctor. The last thing you want to do is take your symptoms for granted, especially if you are at risk of diabetes.
How to Maintain Normal Blood Glucose Levels?
If you aren’t at risk of developing diabetes due to genetic predisposition, maintaining normal blood glucose levels is fairly easy.
All you have to do is be mindful of your lifestyle choices and dietary habits.
Some of the effective tips and precautionary insights include:
- Instead of eating refined foods, switch to whole-grain foods high in fiber and have a low glycemic index.
- Indulge in regular exercising as per your health and well-being. Even a morning or evening walk is considered good for your well-being if you lead a sedentary lifestyle.
- Unless instructed otherwise by your doctor due to other health complications, ensure that you drink enough water throughout the day. Hydration is key to regulating your blood glucose levels.
- If you are on medications for diabetes or on insulin, discuss changing or adjusting the dosage as per your current blood glucose levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Is blood sugar higher 1 hour or 2 hours after eating?
Your blood sugar levels will elevate 1-2 hours after eating, but the normal range should be less than 180 mg/dL. The levels increase due to the glucose from the ingested food.
-
Does water lower blood sugar?
Drinking optimal levels of water throughout the day rehydrates the blood and can potentially reduce blood glucose levels significantly.
-
What should normal glucose levels be?
Before meals, the normal glucose levels in adults should be less than 100mg/dL and under 180mg/dL two hours after the meals.
Conclusion
Blood glucose levels are indicative of your body’s overall metabolic functions. If you are at risk of diabetes or have a family history of or are suffering from, regular testing for the blood glucose levels is crucial to one’s well-being. However, maintaining normal blood glucose levels isn’t as difficult. All you have to do is introduce healthy lifestyle and dietary habits as we mentioned in the guide. Also, if you notice something amiss with your body, don’t delay and consult a doctor to rule out any complications.