Is Jaundice Contagious? Check the Facts

Medically Reviewed By
Dr. Geetanjali Gupta
Written By Sheena Mehta
on Aug 24, 2024
Last Edit Made By Sheena Mehta
on Jul 19, 2025
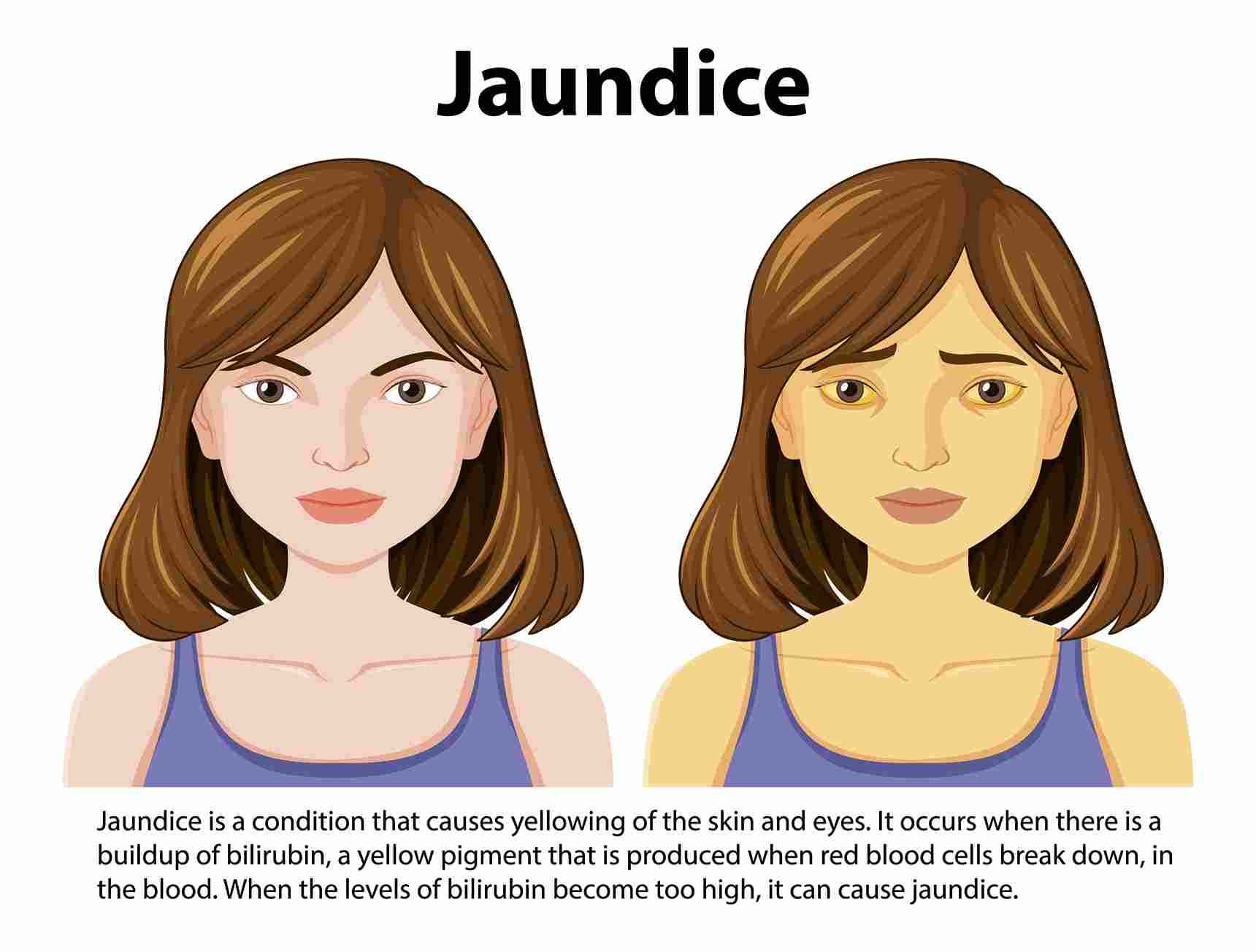
Overview
Jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and eyes, indicating underlying liver or bile duct issues. Jaundice itself is not a disease. It underlines several potential health issues. You tend to worry about the contagious nature of jaundice. So, is jaundice a contagious or infectious condition? Let's do an in-depth analysis of this question and verify the facts.
10 Common Symptoms of Jaundice
Listed below are common symptoms of jaundice, including:
- White eyes & yellow skin
- Darker pee
- Paler poop
- Itchy skin
- Feeling feverish
- Abdominal pain
- Fatigue or weakness
- Nausea & Vomiting
- Appetite loss
- Unintentional weight loss
What is the main reason for jaundice?
Bilirubin is a brownish-yellow pigment produced through the breakdown of red blood cells. Icterus, or Jaundice, occurs when the blood contains high bilirubin levels. Conjugated bilirubin is excreted into bile. However, if the bilirubin accumulates in the body, it can result in jaundice.
4 Conditions that Cause Jaundice are:
- Liver Diseases: The conditions like hepatitis, cirrhosis, and cancer of the liver can cause jaundice.
- Blockage of the bile ducts by gallstones: These stones can prevent bilirubin from being eliminated and cause it to accumulate in the blood.
- Hemolytic anemia causes an excess of bilirubin because red blood cells break down too quickly.
- Jaundice in newborns is a common condition brought on by the liver's immaturity, which results in a temporary buildup of bilirubin.
Does jaundice spread?
To answer the question directly, jaundice is not contagious in and of itself. Jaundice is not a disease but rather a symptom that cannot be passed from one person to another. Jaundice, on the other hand, has a variety of underlying causes, some of which are contagious. It is essential to understand the difference between jaundice and its causes.
Jaundice Causes That Are Contagious:
Here are four causes of contagious jaundice. Have a look!
- Viral Hepatitis:
- Hepatitis A occurs when a person has not been vaccinated for the hepatitis A vaccine. Contaminated food and water can typically spread this type of hepatitis. It is a disease that is spread in areas where a quality water supply is not accessible. A Hepatitis A infection can cause jaundice.
- Hepatitis B and C can happen by blood of someone who has the disease, such as through unprotected sex, sharing needles, and mother-to-child transmission during childbirth. Even though hepatitis B and C can cause jaundice. The disease itself is not contagious.
- Hepatitis D occurs when a person already has the hepatitis B virus and comes into contact with infected blood. An individual cannot have hepatitis D without hepatitis B.
- Hepatitis E occurs through contaminated drinking water. Jaundice may occur as a symptom of a hepatitis E infection.
- Mononucleosis Infectious is brought on by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). It can occasionally result in jaundice. The virus is spread primarily by saliva, but the resulting jaundice is not a contagious symptom.
- Leptospirosis. Also known as Weil’s disease, it can cause jaundice by coming in contact with water contaminated by the urine of infected animals, spreading this bacterial infection. It is the bacteria, not the jaundice, that spreads.
- Gilbert syndrome can happen when a defective gene is passed on from parent to child.
6 causes of jaundice that are not contagious
Many causes of jaundice are not contagious. It means they cannot be communicated or spread from one to another. Here is a list of six causes of jaundice that are not contagious. These include:
- Alcoholic liver disease occurs with the overconsumption of alcohol, resulting in jaundice.
- Cirrhosis is a condition characterized by scarring of the liver. It is caused by long-term liver damage. Chronic liver diseases like alcohol abuse or hepatitis can cause jaundice.
- Gallstones are responsible for blocking bile ducts and can cause jaundice.
- Medications: Certain over-the-counter and prescribed medicines, like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or acetaminophen, can cause jaundice.
- Hemolytic anemia. In this condition, the red blood cells (RBC) are destroyed. Further, this can cause jaundice but is not contagious.
- Newborn Jaundice: This type of jaundice is neither permanent nor contagious. It is a common condition in newborn babies that occurs due to the liver’s immaturity.
Also read: https://redcliffelabs.com/myhealth/liver/jaundice-types-symptoms-causes-and-treatment/
5 Common Myths and Facts about Jaundice
Here are five common myths about jaundice that you may like to know:
Myth No. 1: Jaundice: It is contagious
All forms of jaundice are contagious.
Fact: Jaundice itself doesn’t spread. It is a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as viral hepatitis, which can be contagious.
Myth 2: Jaundice: It can be communicated through physical contact.
It is a common misconception. Jaundice cannot be spread through physical contact.
Fact: Jaundice cannot be spread through sharing utensils or coming into contact with someone with jaundice. Jaundice is contagious only when the underlying cause is a transmissible infection.
Myth 3: Jaundice can be spread by eating contaminated food.
It is a myth that one can get jaundice by eating contaminated food.
Fact: One may get hepatitis A when one eats or drinks contaminated food, which may cause jaundice. It is not the jaundice that is contagious but the infection.
Myth 4: Jaundice patients should eat only boiled foods.
It is a myth that jaundice patients should eat bland or boiled food as it is easy to digest.
Fact: A jaundice patient should consume low-fat foods that are also high in carbohydrates and easy to digest. This is because a person with jaundice can’t process and eliminate toxins efficiently.
Myth 5: Home remedies can cure jaundice.
If you are suspected of having jaundice, home remedies can help relieve some symptoms, such as nausea, itching, or fatigue.
Fact: Consult your healthcare provider. He is the best person to identify the problem and give the appropriate treatment.
5 Preventing Jaundice Causes That Are Contagious:
It is essential to take preventative measures because certain contagious infections can cause jaundice.
- Vaccination: Get vaccinated for hepatitis A and B to lower your risk of contracting these viruses and, consequently, your risk of developing jaundice.
- Safe Practices: In cases of hepatitis B and C, don't share needles, make sure that blood products are screened before they are given out, and have safe sex.
- Good hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly to stop the spread of hepatitis A and E.
- Safe Water for Drinking: In areas where hepatitis E is widespread, you must drink clean water and ensure that food is cooked properly.
- Avoiding Contaminated Water: To prevent leptospirosis from contracting, do not swim in or consume water that might contain animal urine.
Conclusion:
Jaundice is not contagious. It is a symptom of an underlying condition, which may be contagious in some cases. To know if jaundice is contagious, you must know what causes it. Many other causes of jaundice are not contagious and do not pose a risk of transmission, even though conditions like viral hepatitis can spread from one to another and potentially result in jaundice.
By distinguishing between jaundice and its underlying causes, we can better address concerns and ensure that those affected get the proper treatment, care, and support.



