Urinary Tract Infection (UTI): Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment

Medically Reviewed By
Dr. Ragiinii Sharma
Written By Prekshi Garg
on Jun 1, 2022
Last Edit Made By Prekshi Garg
on Jan 9, 2025
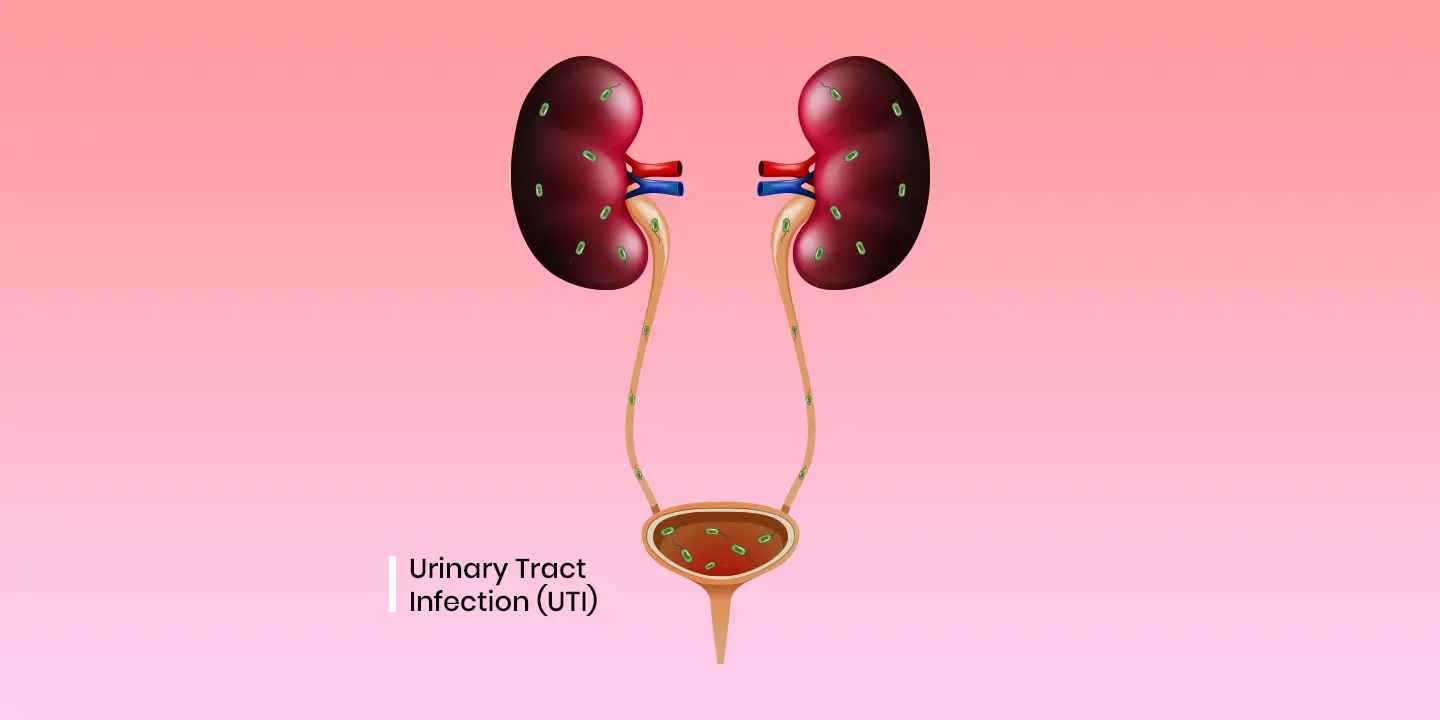
Urinary tract infection or UTI, as the name suggests are the infections occurring in any part of the urinary system. This is one of the most common infections that can occur in both males and females of all ages. However, in general females are more prone to urinary tract infection as compared to males and adults have a greater chance of developing urinary tract infection than young people. Approximately 150 million people every year are diagnosed with urinary tract infection across the globe. According to research, the risk of development of urinary tract infection in females is 60% whereas in males it is only 13% in their entire lifetime. According to sources, the occurrence of urinary tract infection in females is around 40% and in males, it is around 12%.
|
Are you brushing aside recurrent symptoms of frequent urination, burning sensation while peeing, and dark yellow coloration of the urine? If yes, you are likely ignoring the early signs of a UTI. Don’t take the symptoms for granted since an untreated UTI can leave to complications down the road. Get tested when things start feeling uncomfortable. Early testing leads the way to a quicker recovery. |
With such widespread occurrence of these infections, it is very important to diagnose it as early as possible for better treatment and prevention of recurrent urinary tract infection. It is also beneficial to understand how to take better precautions. In this article, let us talk about the different parts of your urinary tract where the infection can occur as well its most common symptoms, causes, treatment, and prevention.

What is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
The infection in any part of the urinary system is known as a urinary tract infection or UTI. It is not normal for the urine to contain bacterial contamination over a certain saturation. However, bacterial contamination can occur in the urinary tract due to exposure to bacteria from outside the body. The bacterial infection can affect any part of the urinary system. Depending on the part of the urinary system affected, the urinary tract infection is given different names.
- If the infection occurs in the urethra, it is known as urethritis. The urethra refers to the tube that carries the urine outside your body from the bladder.
- Pyelonephritis refers to the infection of the kidneys. The kidney as we all know is the organ involved in removing the waste and water from your blood. Thus, kidneys are rightly known as the filters of your body.
- Cystitis refers to the infection of the urinary bladder. The urinary bladder acts like a storage container that collects the urine until it is moved out of your body.
What are the symptoms of urinary tract infection (UTI)?
The signs and symptoms of a urinary tract infection usually vary depending upon the part of the urinary system affected and the severity of infection.
General symptoms of Urinary Tract Infection
There are certain symptoms that usually occur in any type of urinary tract infection. These symptoms can be an indication of the infection. The most common symptoms of urinary tract infection include:
- A persistent and strong urge to urinate
- Experiencing a burning sensation while urinating
- Increased frequency of urination that passes only a small amount of urine at frequent intervals
- Passing urine that appears cloudy
- The presence of blood in the urine can be indicated by bright pink, red, or cola-colored urine
- Excreting urine that has a strong smell
- Women might also feel pain in the centre of the pelvis region
Symptoms of Acute Pyelonephritis
Acute pyelonephritis refers to the infection when it reaches within the kidneys. There are certain symptoms that specifically occur when your kidneys are affected by a bacterial infection. These specific symptoms include:
- High fever
- Nausea
- Chills and shaking
- Vomiting
- Back pain or pain on the sides or flank
Symptoms of Cystitis
Cystitis refers to the infection of the urinary bladder. There are certain symptoms that specifically occur when your urinary bladder is affected by a bacterial infection. These specific symptoms include:
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen region
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Feel pain while urinating
- Feeling a pressure exerted on the pelvic area
- Presence of blood in the urine
Symptoms of Urethritis
Urethritis refers to the infection of the urethra. There are certain symptoms that specifically occur when your urethra is affected by a bacterial infection. These specific symptoms include:
- Abnormal discharge from the vaginal area
- Feeling a burning sensation while urinating
What are the causes of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
The main causative agent of infections in the urinary tract is bacteria. This happens when the bacteria enter the urinary tract of your body through the urethra and begin to multiply in the urinary bladder. It is common when an individual is exposed to public washrooms or unhygienic urinary conditions. Most of the time, the urinary system keeps these invading microorganisms out of the tract, however, sometimes they may enter the tract causing infections.
- The infections in the urinary bladder are generally caused due to the contamination of the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli). E.coli is one of the most common bacterial contaminations usually found in the urinary tract. However, apart from E.coli, some other bacteria may also be present.
- The infection in the urinary bladder can also occur due to the sexual intercourse
- The urethra is infected when the contaminating microorganisms grow, divide, and spread from the anus to the urethra.
- The closeness between the vagina and the urethra makes the females more prone to the development of sexually transmitted diseases like gonorrhea, herpes, mycoplasma, and chlamydia.
A certain group of people is more prone to the development of urinary tract infections. The high-risk factors of UTI include:
- As your age increases, your chances of developing urinary tract infection also increases.
- If you have had a prolonged bed rest due to surgery or any other medical condition, that has reduced your mobility
- Presence of stones in your kidney
- A previous infection in the urinary tract
- Obstructions like kidney stones, enlarged prostate gland, and cancer that can block the urinary tract
- Prolonged use of urinary catheters can also make the bacterial contamination easier
- People who have diabetes
- Pregnant women are also more prone to urinary tract infections
- If your urinary structures are abnormally developed since birth
- If you have a weak immune system
- If you have an enlarged prostate
Urinary tract infection is more common in females than it is in males. This is because of the different anatomy in both males and females. These differences include:
- Short urethra: In females the urethra and vagina are very close to each other, which minimises the size of the urethra. The shorter the urethra, the greater are the chances of the female encountering the urinary tract infection. This happens because bacteria are naturally present around the anus and the vagina which makes females highly susceptible to infection. Also, the invasive microorganisms have to travel less distance to reach the urinary tract as compared to the females.
- Sexual intercourse: The pressure exerted during the penetrative sexual intercourse on the urinary tract of the females can also allow the bacteria to move from the anus into the urinary bladder. Not only vaginal sex, but even oral sex can increasing the risk of infection by introducing bacteria into the urethra. However, you can reduce the risk of infection by urinating after sexual intercourse.
- Use of condoms during sexual intercourse: Condoms are no doubt very essential during a sexual intercourse, but uring non-lubricated latex condoms cause irritation to your skin during a sexual intercourse thereby, increasing your chances of infection. You can prevent this irritation by using a water based lubricant during the intercourse and avoiding the usage of spermicide coated condoms.
- Diaphragm: In some cases, diaphragms put a certain pressure on the urethra due to which the urinary bladder does not empty properly causing an increased risk of bacterial growth and infection.
- Decreased levels of estrogen: After the menopause hits a woman, the levels of estrogen in your body starts decreasing. The decreased levels of oestrogen affects the normal bacteria present in your vagina, thereby, increasing the risk of urinary tract infections.
How can Urinary Tract Infection be treated?
The treatment plan for urinary tract infection depends on the causative agent causing this infection.
- The bacterial infections are treated using antibacterial drugs, whereas antiviral and antifungal drugs are used to treat the virus and fungi infection.
- The oral antibiotics are given to treat the infections occurring in your lower tract.
- The intravenous antibiotics are used for the treatment of infections occurring in the upper urinary tract.
- The medicines for urinary tract infection are prescribed for the shortest possible duration to prevent development of antibiotic resistance among the microorganisms.
- The course of antibiotics and its duration that best suits your health condition is determined by your urine culture.
The recurrent urinary tract infections are very common. It is estimated that 1 in every 5 females have recurrent UTI. The recurrent urinary tract infection is known as chronic UTI and it generally occurs because of different stains of bacteria or because of antibiotic resistant bacteria. The treatment protocols that can be advised by the doctor for the treatment of chronic UTI include:
- A very small dose of antibiotics for a prolonged period
- Antibiotics can be taken for 1-2 days once the symptom appears
- Taking a single dose of antibiotic after the sexual intercourse.
- A non-antibiotic prophylaxis treatment can also be considered.
How can Urinary Tract Infections be Prevented?
The recurrence of urinary tract infection can be prevented if you follow a healthy lifestyle. Certain tips that can help you in preventing urinary tract infection include:
- Try emptying your urinary bladder completely whenever you feel an urge to urinate.
- After using the toilet, always wipe yourself from front to back.
- Instead of taking baths, choose showers more frequently
- Increase your intake of water. This will help in flushing out toxins from your body
- Scented bath products, douches, and feminine hygiene spray increase irritation in private parts, so avoid the usage of these products.
- Before a sexual intercourse, cleanse your genitals thoroughly
- Urinate after having a sexual intercourse, to decrease your chances of getting a urinary tract infection.
- Choose the birth control method wisely. You may need to change your method if you are using diaphragm, spermicidal jelly, or unlubricated condoms for sex control. This is because diaphragms can cause an increase in the bacterial growth, whereas spermicidal jelly and unlubricated condoms can cause irritation in your urinary tract.
- Prefer wearing cotton underwears and loose fitted clothes, so that the moisture does not get trapped in your private parts. This is essential because trapped moisture provides a perfect environment for the microorganisms to grow.
Takeaway
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common forms of infection prevalent in India. These infections can affect any part of your urinary tract system. It is very common for one to get urinary tract infection, therefore, it is essential to know the symptoms of UTI so that they are diagnosed at an early stage. Urinary tract infections can recur after sometime, therefore, in such cases you should know how to prevent the occurence of these infections. Now that you know all about the types of urinary tract infection, their symptoms, causes, and treatments, you will better be able to analyse your health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What causes frequent UTIs in females?
The different anatomy of males and females, make females more prone to the development of urinary tract infections.
-
Can UTI go away on its own?
Certain urinary tract infections can go away on their own without the need of any antibiotics. However, certain other infections may require antibiotic treatment for its complete removal.
-
What increases the risk of UTI?
The presence of stones in the kidney or an enlarged prostate gland can increase your risk to the development of urinary tract infection by trapping the urine in the bladder and prohibiting its excretion from the body.



