Hypothyroidism In India: Symptoms, Cause, and Treatment

Medically Reviewed By
Dr Divya Rohra
Written By Prekshi Garg
on May 10, 2022
Last Edit Made By Prekshi Garg
on Mar 17, 2024
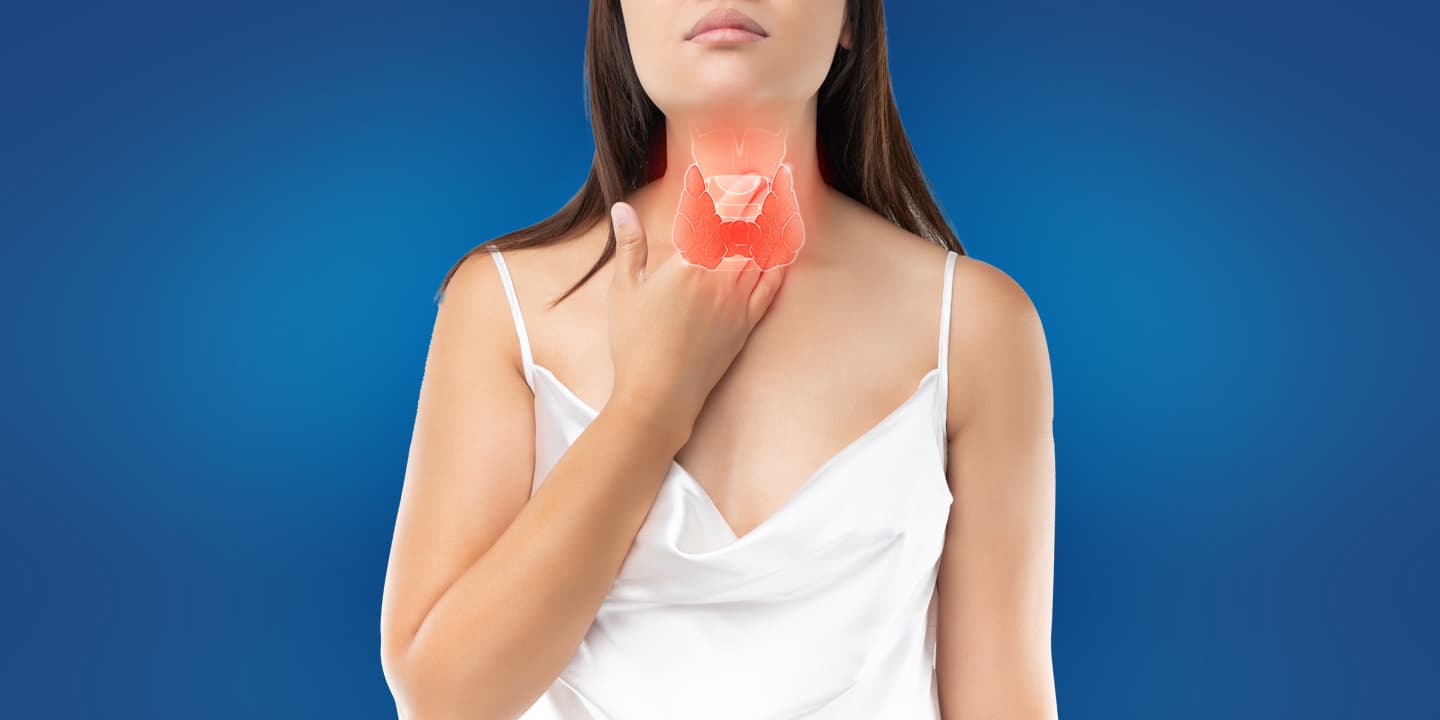

The thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland in the thoracic region is an important endocrine gland that makes the thyroid hormones. Thyroid hormones regulate many activities in the body, including how fast you can burn calories and heart rate control.
Thyroid tests help diagnose different thyroid hormones. They help determine the reason for excess thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism) and low thyroid hormone generation (hypothyroidism). The thyroid tests include blood analysis of thyroid hormones and imaging tests of the thyroid gland.
|
You can regard your symptoms of sudden weight gain, tiredness, irritability, low energy levels, constipation, etc. as possibilities of hypothyroidism. If you have a familial history of the condition, we’d recommend getting your thyroid hormone levels tested before it takes a turn for the worse. |
In this Article
Thyroid hormone and thyroid functioning
Thyroid hormone, made by the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland, is located in the front neck region above the collar bone. The thyroid gland releases the thyroid hormone into the blood, which is circulated to all the tissues and organs. The functions of the thyroid hormone include:
- Helping the body’s cells use energy
- Regulating the body’s temperature
- Controlling the activities of the brain, heart, muscles, and other organs.
The Thyroid gland generates two main forms of thyroid hormone.
- Thyroxine (T4)- A primary form of thyroid hormone gets eventually converted to the T3 form of thyroid hormone in certain tissues, liver, and brain by an iodine atom elimination.
- Triiodothyronine (T3)- the second form of thyroid hormone, accounts for only 5% of the circulating thyroid hormones.
Thyroid hormone produced by the thyroid gland is regulated by another endocrine gland called the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) into the blood, signalling the thyroid gland to make T4 and T3.
Similar to sense organs, the pituitary glands sense the requirement of thyroid hormones and accordingly signal TSH release. Once the T4 levels in the blood reach the required level, the pituitary stops TSH production, and thus, the thyroid hormone also halts T4 generation.
Since the pituitary hormone TSH controls the thyroid gland functioning, TSH levels along with T3 and T4 levels in the blood, are analysed during thyroid testing.
Most of the thyroid hormones generated circulate in the blood and are bound by protein. Only a small fraction of the hormone enters the tissues and organs to bring about the required biological effect. Thyroid tests measure the total thyroid levels (protein-bound and free) or only the free thyroid hormone levels (without protein binding).
Thyroid hormones analysed during a blood test
Thyroid level checks in the blood are routinely performed blood tests where the lab technician draws a certain amount of blood from the body and measures the levels of various thyroid hormones such as,
TSH or Thyroid Stimulating Hormone
TSH or Thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood acts as an early signal system. Even before the thyroid hormones are measured, the TSH levels indicate hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. TSH levels also help determine how well the thyroid gland is functioning.
A normal TSH value means that the thyroid gland functions are optimal. Blood with high TSH levels means that the thyroid gland is not performing to the level it must or causing primary hypothyroidism. A low TSH level signifies that the thyroid gland is making more than the required thyroid hormone, leading to hyperthyroidism. However, a low TSH level also indicates an abnormality in the pituitary gland or a condition called central hypothyroidism.
Thyroxine or T4 hormone
T4 tests include two aspects. One is the Total T4 test, measuring the protein-bound and free thyroxine (T4) hormone in the blood. And the second is the Free T4 or FT4, measuring the protein-free T4 entering the tissues and organs.
Total T4 levels vary due to health conditions and medications that change the levels of protein-binding T4 hormones. Some of the common reasons for an increased thyroxine level are hormones such as Oestrogen, oral contraceptive pills, pregnancy, liver disorders, and hepatitis C infection. Anabolic steroids, testosterone, and androgens cause reduced protein binding T4 and total T4 levels.
In natural conditions like pregnancy, free T4 levels, FT4 or Free T4 index (FTI) give more precise outcomes on the thyroid gland functioning.
Triiodothyronine or T3 hormone
T3 tests measure the levels of T3 hormone converted from T4. Similar to T4 tests, total T3 tests measure both bound and free triiodothyronine levels. T3 tests help understand the line of treatment for hyperthyroidism and determine the severity of high thyroid levels in the body.
Hyperthyroidism is often connected to high T3 levels. The proportion of T3 and T4 varies and can help diagnose thyroid conditions. For instance, an increase in T3 to T4 indicates Grave’s disease. Certain medical conditions and steroids lead to T4 conversion to T3. T3 levels are usually low in people with hypothyroidism. Evaluations of free T3 are often not preferred and reliable.
Additional blood tests for Thyroid
Other thyroid hormone tests that may be a part of standard thyroid checkups or opted when required to evaluate possible causes of certain conditions include:
- Reverse T3 or RT3 tests: This test measures the inactive form of the T3 hormone in the body. This test can help detect problems with thyroid control or understand problems with abnormal thyroid hormones not related to the thyroid.
- Thyroglobulin or Tg tests: Measures thyroglobulin, a protein made by the thyroid gland to help guide thyroid cancer treatment. In the journal, Thyroid, a research article shows that 4% of people with Tg protein under 1 could see a recurrence of cancer after five years.
- Thyroid antibodies: Thyroid diseases can be due to autoimmune factors where the immune system, by mistake targets and attacks the healthy thyroid cells. The antibodies produced are checked and matched to find if the condition is an autoimmune disease.
The three common antibodies associated with the autoimmune thyroid condition are:
- Thyroid peroxidase Antibodies tests (TPOAb): In cases with high TSH and low T4 levels, this test can help confirm Hashimoto's disease. A shoot-up of TPOAb levels is also observed in women with postpartum thyroiditis.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor Antibody tests (TRAb): These tests can help detect Graves' disease, and can confirm the diagnosis of toxic multinodular goiter. The test done during the last trimester of pregnancy checks the baby's risk of developing Graves' disease or hyperactive thyroid.
- Thyroglobulin Antibody tests: The thyroglobulin antibodies in the body respond to thyroglobulin. These antibody tests help check autoimmune conditions and confirm thyroid cancer treatment test results.
Normal and abnormal Thyroid hormone test ranges
The normal ranges of thyroid hormone differ according to age, underlying conditions, and gender. The normal range values also vary during pregnancy, and among laboratories.
| Thyroid hormone tested | Reference range |
| TSH | 0.5 to 5.0 mlU/L |
| FT4 | 0.7 to 1.9ng/dL |
| Total T4 | 5.0 to 12.0 μg/dL |
| Total T3 | 80 to 220 ng/dL |
| Free T3 | 2.3 - 4.1 pg/mL |
| Tg (serum) | 0-30 mg/m |
In case of pregnancy, a history of thyroid cancer, or pituitary gland disease, and in older ages, TSH ranges differ. Higher or lower than normal ranges are considered abnormal ranges.
| Abnormal Thyroid hormones | Result interpretation |
| High TSH, low FT4 | Primary hypothyroidism, underactive thyroid |
| High TSH, normal T4 | Subclinical hypothyroidism |
| Low TSH, high FT4 | Primary hyperthyroidism, overactive thyroid |
| Low TSH, normal T4 | Early or mild hyperthyroidism |
| Low TSH, high T4
Followed by, High TSH, low T4 | Thyroiditis (Thyroid Inflammation) |
| Low TSH, low thyroid hormones | Problem of the pituitary gland functioning of pituitary disorders. |
While the test results and reference ranges are mentioned, it is also important to know that these reference range values vary between laboratories and are likely to differ.
Abnormal thyroid function associated conditions
Here is a discussion of various thyroid conditions caused due to abnormal thyroid functioning.
Primary Hypothyroidism
Primary hypothyroidism is detected when the thyroid test results indicate high TSH and low FT4 or thyroid hormone levels. This condition is seen when the thyroid gland makes very less thyroid hormone or when the thyroid glands are underactive. Some of the symptoms indicating hypothyroidism include:
- Constipation
- Increase in weight
- Delay or slowed thinking
- Low energy levels
- Body sensitive to cold
- Muscle weakness, pain, tenderness, and stiffness
- Dry skin
- Hair thinning
- Slow heart rate
- Depression
- Irregular and heavy menstruations
- Swollen thyroid gland (Goitre)
Hypothyroidism mostly affects women in their middle age or old age. However, anybody, including infants, can develop this condition. Infants born with abnormally functioning thyroid, or without a thyroid gland may have signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism such as,
- Jaundice- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes jaundice.
- A protruding tongue
- Breathing difficulties
- Hoarse cry
- Umbilical hernia
As infants grow, the disease can progress to cause trouble while feeding and may lead to developmental delays. Some of the other noticeable symptoms are:
- Constipation
- Poor muscle development
- Poor growth, short stature
- Delayed development of permanent teeth
- Delayed puberty
- Too much sleepiness
- Severe physical and mental retardation.
Subclinical hypothyroidism, also known as early or mild hypothyroidism, is when there is a persistent increase in TSH levels, but the FT4 levels are relatively normal. Subclinical hypothyroidism also needs timely treatment or can contribute to heart problems.
Primary Hyperthyroidism
Primary hypothyroidism is when the thyroid test results indicate a low TSH and a high FT4 level. This condition is observed when the thyroid gland gets overactive to make or release excess thyroid hormones. Some of the symptoms of hyperthyroidism to look out for are:
- Nervousness, anxiousness, irritation
- Excess loss of weight
- Palpitations or rapid and irregular heartbeats
- Increased appetite,
- Restlessness,
- Trembling hands and legs,
- Increased sensitivity to heat,
- Muscle weakness, fatigue,
- Skin thinning, brittle hair,
- Changes in menstrual cycles,
- Swelling at the base of the neck, enlarged thyroid gland (Goitre),
- Frequent bowel movements,
- Disrupted sleep.
Subclinical early or mild hyperthyroidism is observed when the TSH levels are persistently low while the FT4 levels are normal. Such conditions, if left untreated, can lead to osteoporosis and abnormal heart arrhythmia.
Thyroiditis
Thyroid inflammation or thyroiditis causes damage and swelling of the thyroid gland. People with thyroiditis observe two types of test interpretations. One is a brief period of hyperthyroidism with low TSH and high FT4 or Total T4, followed by hypothyroidism with increased TSH and low FT4 or Total T4 levels.
Sometimes, in cases of postpartum thyroiditis, or infections, the condition is temporary and requires no specific medications.
Other cases of thyroiditis may be due to cancer immunotherapy, which is permanent and requires long-term treatments, including thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Pituitary disease
The pituitary disease is seen when the test results show low TSH and low FT4 levels. The condition may require further pituitary hormone checks, and imaging tests and is generally treated with thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
Factors that can affect thyroid test results
Endocrinologists help monitor thyroid levels along with other associated endocrine hormones. They help you understand the thyroid test results and order additional tests if required. Factors such as medications, supplements, and other medical conditions, can influence the test results. So, it is important to inform your endocrinologists or doctor about the medications and associated non-thyroid medical conditions, if any.
Sometimes, if there are any discrepancies in the thyroid test, your doctor may advise repetition of the test to confirm the previous result. These thyroid tests are a must to understand the short term and long term medications, measures to balance thyroid levels and manage the abnormal symptoms.
Conclusion
Thyroid hormones are necessary to help the body cells utilise energy to carry out bodily activities. Thyroid tests indicate whether or not the thyroid functions are regular. Abnormal thyroid test results may require further analysis and regular monitoring to maintain normal thyroid hormone levels.
Endocrinologists specialise in endocrine glands and hormone understanding, help determine how to go about with abnormal thyroid levels, and manage hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What blood tests are done to test thyroid?
The blood tests done to assess thyroid hormones include:
- TSH test: Measures the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone produced by the pituitary gland that triggers thyroid hormone production and regulates thyroid functioning.
- T3 and T4 tests: Check the levels of different thyroid hormones that regulate how the body uses the energy.
- TSI test: Measures thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce T3 and T4 hormones.
- Antithyroid antibody test: Measure the levels of antibodies that can destroy thyroid tissue or cells producing thyroid hormones.
-
What more should I know about thyroid tests?
Thyroid hormone levels change during pregnancy and due to certain medical conditions. They also differ concerning the age and gender of an individual. Your healthcare provider will help monitor and assess thyroid levels. They will guide you on ways to balance these hormones and help maintain normal ranges.
-
What is a low thyroid level?
A TSH level above 5.0 mU/L, indicates an underactive thyroid gland or hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland produces too little thyroid hormones. The overall thyroid hormone levels go low in such conditions.